
The average consumer is spending five hours per day on their smartphones and this number is only going up.
We do everything on our phones these days, from shopping to browsing social media and managing our businesses.
This is why it’s more important than ever to optimize the user experience to keep people on your app for longer periods, enjoying it more, and sharing it with friends.
If you’re trying to optimize your mobile app, I’m sure you’ve already tinkered with the layout, fonts, copy, and more, but there’s one thing you probably haven’t…
Mobile deep linking.
It’s a small detail that can drastically enhance how users engage with your app but few are taking advantage of it.
That’s why I’m going to be teaching you what mobile deep linking is, why you need it, and how you can implement it yourself.
Let’s dive in.
What is mobile deep linking, anyways?
Mobile deep linking is the practice of funneling users deeper into your app through the use of a uniform resource identifier or URI for short.
This allows mobile app developers to push to a specific page within an application versus simply opening it.
Think of it as a website URL.
If you were trying to sell a product, would you want users landing on the homepage or being forwarded to a sales page found deeper in the website?
The latter, of course.
By helping users go to a certain page within an app, you’re making the customer journey easier by getting them closer to the end goal sooner.
Here’s a visual of what the process looks like:
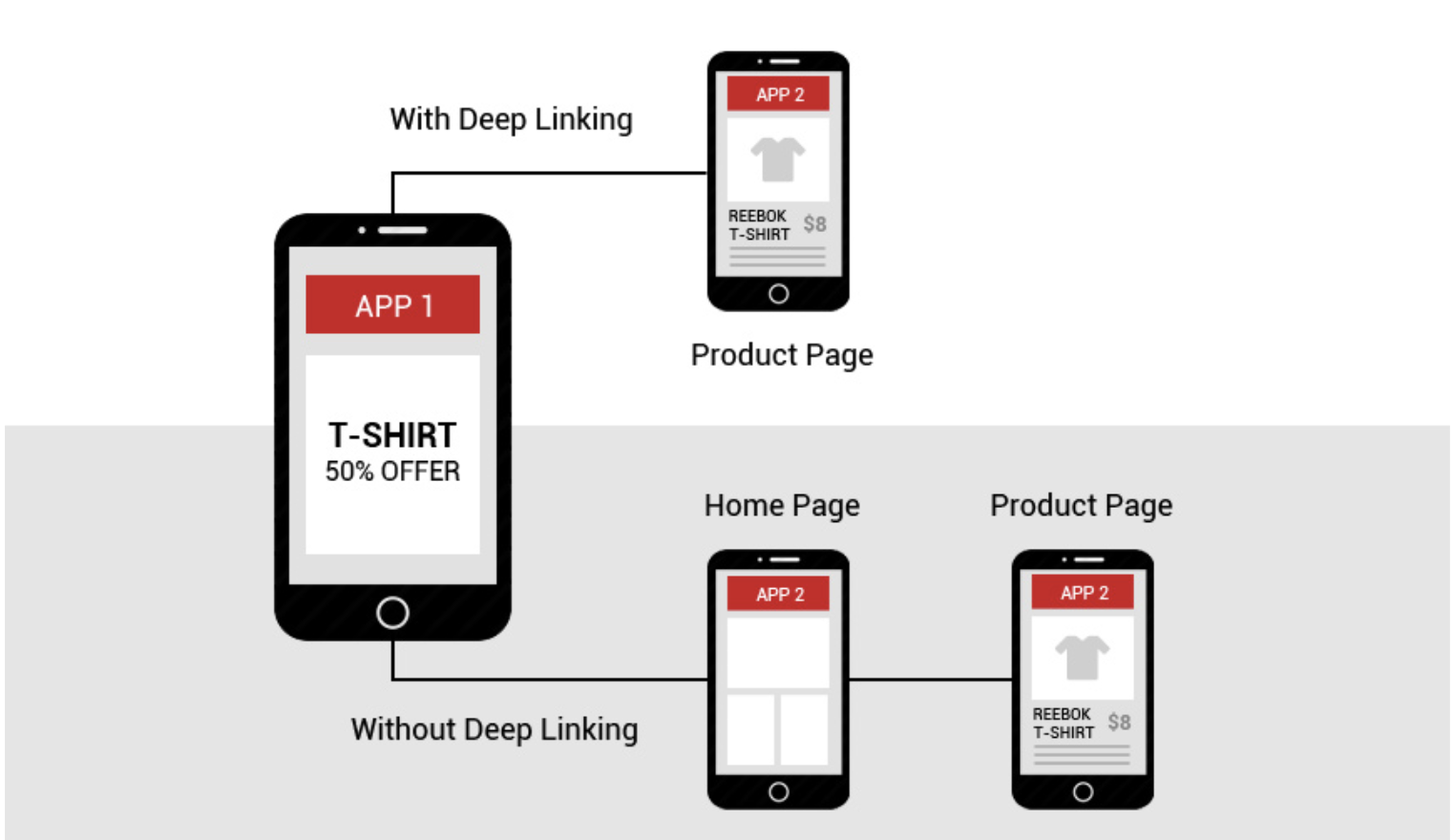
While it might seem simple, mobile linking comes in three different forms that you need to be aware of. They include the following:
Standard deep linking
This is the straightforward deep linking that forwards a user to a specific part of the app. It’s also known as universal linking.
It only works if the customer already has the app installed.
The problem is within traditional linking is that when a user clicks a link, it won’t open the mobile app, but rather directs them to the browser version.
If someone is on a mobile device, the app version will always be more optimized and streamlined.
Here’s what happens if you search for my Instagram on Google for example with the app installed.
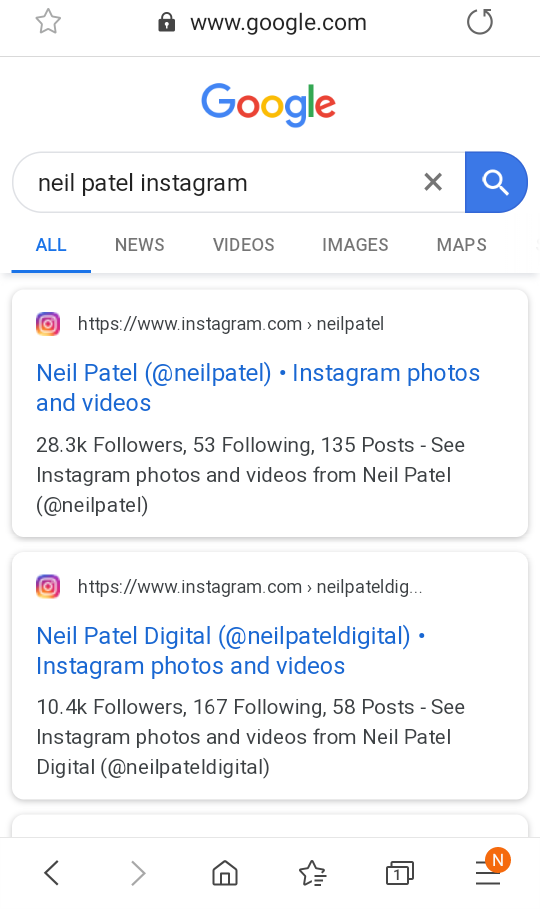
The results appear to be the exact same whether you have the Instagram app or not, but clicking it opens up the app seamlessly.
This is a good example of basic deep linking.
Someone that doesn’t have the Instagram mobile application installed will be given an error or redirected to a fallback page.
Deferred deep linking
This form of deep linking works the same way as standard linking does with the exception that it will direct users without the app to the download location.
This is beneficial because it can help app developers and companies acquire more customers.
Once the app is installed, the user will be referred to where they were originally navigating.
Check out the Skip The Dishes app to see what I mean.
While a user is creating their order, they are able to download the mobile app for Android or iOS.
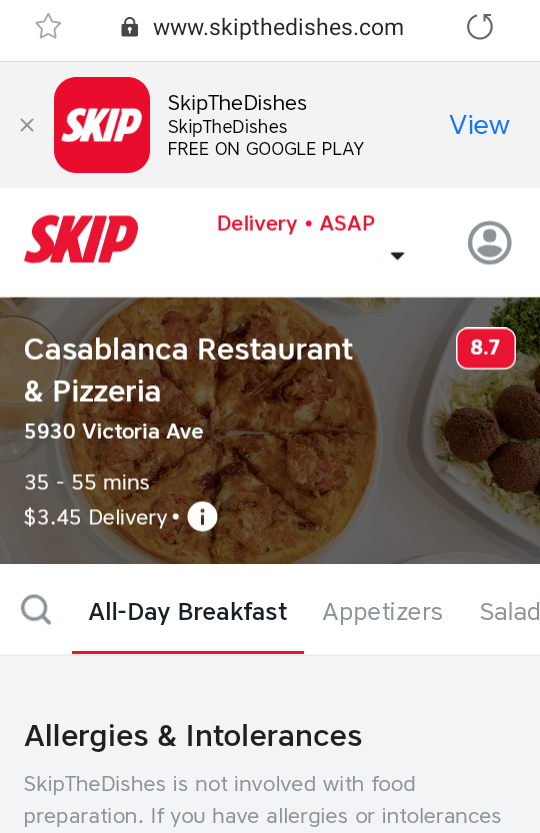
They are forwarded back to the exact step they were taking, except in the mobile app after downloading it.

This means that they don’t have to manually go through the entire process again to get back to where they were.
Contextual deep linking
Contextual deep linking, also known as onboarding, is commonly used for gathering information on customers to personalize the user experience of an app.
Data such demographics, how users navigate to the app, and more is recorded.
The app onboarding process can be different depending on if the user installed via the Google Play Store, the Apple Store, a Facebook campaign, or another source.
A mobile app downloaded through a Facebook Ad might look different than when it’s downloaded through a Google Display Ad, for example.

The landing page is able to be customized through what is known as a deep view in mobile app development.
Just as the deep link forwards users to a specific deeper page in the application, the deep view is the visual result they see that’s different than others.
URI schemes
Deep linking is only doable thanks to what is known as URI schemes. These schemes are similar to how a website URL can direct you to a specific page on a website.
They look something like this:
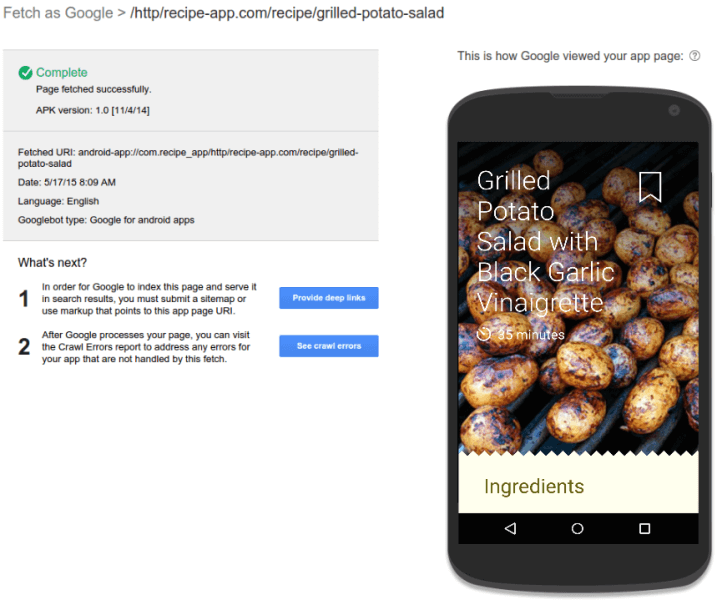
See the fetched URI? Its format is appname://path/to/location.
Custom URIs are simple to set up for developers (Often created by default) and present the opportunity to redirect users wherever you please.
The mobile customer journey and how it applies to deep linking
The mobile buyer’s journey is the individual’s steps a user takes to find, use, and share your application.
It’s similar to the regular funnel a customer goes through when purchasing a product with some small differences you need to be aware of.
Here’s how the various steps in the mobile buyer’s journey can be applied to mobile deep linking.
Discovery
The first step in the mobile customer journey is discovering your app in the first place.
While this can be achieved through strategies like content marketing and SEO, deep linking gives you a nice boost to these tactics.
Google indexes deep links from mobile apps, giving you more opportunities to rank and drive organic traffic.
Users can click the search engine listing and open the link directly through the app instead of an internet browser.
Look at this search for Google Analytics to see what I mean:
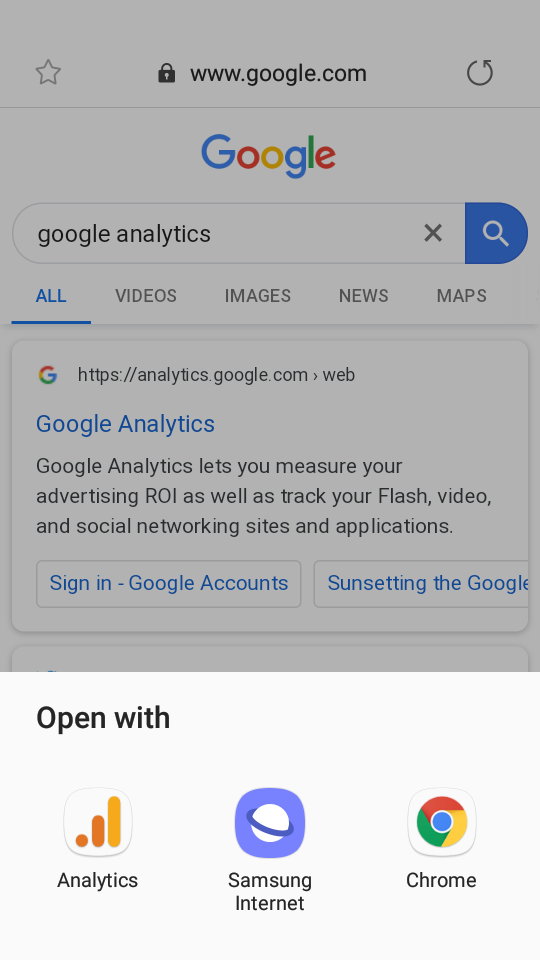
This helps businesses acquire more users and increase brand awareness versus having a single search engine listing.
Check out my video on skyrocketing mobile app organic traffic, and pair it with deep linking for mind-blowing results.
Compare
Once a user has narrowed down a few options, they’re naturally going to want to find the best app by comparing them.
They’ll look at factors such as pricing, ease of use, and features.
Deep linking enables you to push users to the best features of your app, reviews, or customize the experience to make your application better than competitors.
By reducing the number of steps it takes to get to important functions of the app, you’re also decreasing the chance of users bouncing.
Decision
The third step in the mobile buyer’s journey is making a decision and commitment to a single app.
Having a clear value proposition and refined user experience is crucial here.
Better yet, contextual deep linking helps you collect data to make the application as tailored as possible to your buyer’s persona.
Marketing campaigns can also be optimized with this information to improve targeting and performance.
Retain
Once you begin acquiring more users, you need to keep them.
Standard and deferred deep linking will help navigate users back to your app when they are on search engines, social media, and other platforms.
This keeps them using your app more often.
Data that can be collected as a result of deep links will assist you in understanding why and how they use your mobile application.
Doubling down on these is what we call Pareto’s Principle or the 80/20 rule.
This rule can be seen everywhere and defines that 80% of results come from 20% of actions.
In the case of mobile app development, you might discover that users are only engaging with a few features and others are taking up space.
You could hypothetically update the features and pages that are used the most, boosting engagement and retention.
Businesses will miss out on discovers like this if they don’t use deep links to collect information.
Why mobile deep linking matters
I know what you’re thinking.
“Why should I bother with mobile deep linking?”
Let me explain.
It improves the user experience
If you can save the user from going through multiple steps instead of one, why wouldn’t you?
That’s exactly what deep linking does, and improves UX because of it.
You’re making the life of users easier by using deep linking to get them where they want to go faster.
This gives them a better experience and impression with your app as a result.
Here’s what the difference between not using mobile deep linking and taking advantage of it looks like:
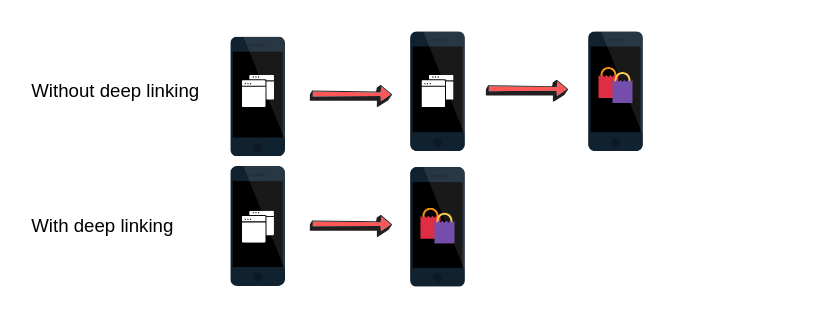
Much simpler, right?
This brings me to my next point.
It increases customer retention and engagement
Wouldn’t it be nice if every user that downloaded your app stay active all year round?
Unfortunately, that’s not how it works.
It’s been found that 55% of users will churn after the first month of use. That means nearly half of the new downloads will be lost.
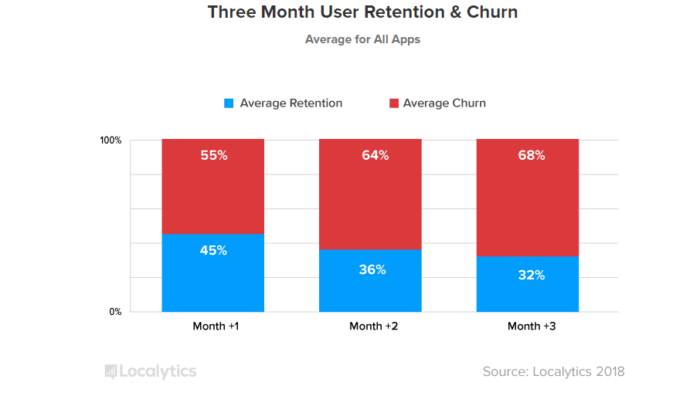
Look at mobile app user retention the same way you approach a website.
It’s common for nearly half of all visitors to leave a website and not take any action.
Do you just sit there and do nothing about it? Of course not!
You implement strategies like email options through popups and exclusive content to capture those users before they leave.
This is precisely what deep linking can be used for but in the sense for a mobile app.
Once a user has visited your app, you can retarget them and use a different style of deep linking to improve their experience.
It improves the onboarding of new users
When a mobile app uses a form of deep linking like the deferred approach, you are capable of acquiring more users.
This is because as a user goes through the mobile browser version of your application, they will be given the option or automatically forwarded to the appropriate download location.
The contextual linking technique can be used to onboard new users in different ways depending on where they originally download the app from.
If you understand that users coming from a Facebook ad campaign regularly navigate to a certain product category, you can push them there automatically.
Furthermore, perhaps users from Google like to learn more about your business first before purchasing.
https://neilpatel.com/blog/mobile-deep-linking/
No comments:
Post a Comment