A report by the lead data watchdog for a large number of tech giants operating in Europe shows a significant increase in privacy complaints and data breach notifications since the region’s updated privacy framework came into force last May.
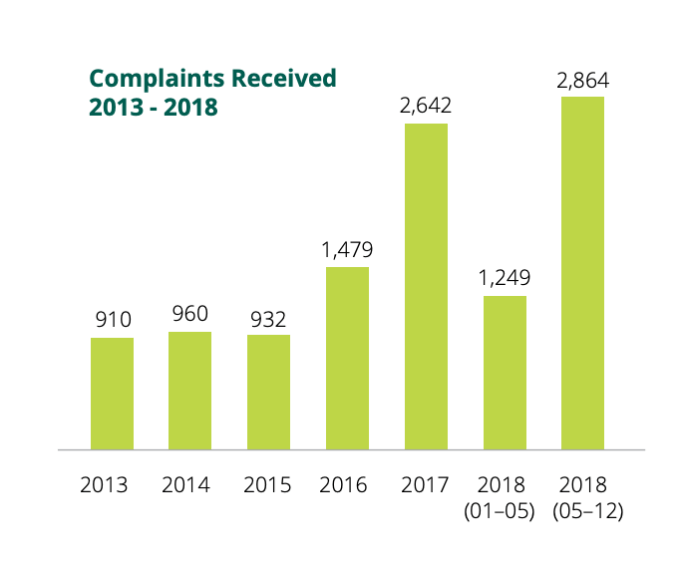
The Irish Data Protection Commission (DPC)’s annual report, published today, covers the period May 25, aka the day the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) came into force, to December 31 2018 and shows the DPC received more than double the amount of complaints post-GDPR vs the first portion of 2018 prior to the new regime coming in: With 2,864 and 1,249 complaints received respectively.
That makes a total of 4,113 complaints for full year 2018 (vs just 2,642 for 2017). Which is a year on year increase of 36 per cent.
But the increase pre- and post-GDPR is even greater — 56 per cent — suggesting the regulation is working as intended by building momentum and support for individuals to exercise their fundamental rights.
“The phenomenon that is the [GDPR] has demonstrated one thing above all else: people’s interest in and appetite for understanding and controlling use of their personal data is anything but a reflection of apathy and fatalism,” writes Helen Dixon, Ireland’s commissioner for data protection.
She adds that the rise in the number of complaints and queries to DPAs across the EU since May 25 demonstrates “a new level of mobilisation to action on the part of individuals to tackle what they see as misuse or failure to adequately explain what is being done with their data”.
While Europe has had online privacy rules since 1995 a weak regime of enforcement essentially allowed them to be ignored for decades — and Internet companies to grab and exploit web users’ data without full regard and respect for European’s privacy rights.
But regulators hit the reset button last year. And Ireland’s data watchdog is an especially interesting agency to watch if you’re interested in assessing how GDPR is working, given how many tech giants have chosen to place their international data flows under the Irish DPC’s supervision.
More cross-border complaints
“The role places an important duty on the DPC to safeguard the data protection rights of hundreds of millions of individuals across the EU, a duty that the GDPR requires the DPC to fulfil in cooperation with other supervisory authorities,” the DPC writes in the report, discussing its role of supervisory authority for multiple tech multinationals and acknowledging both a “greatly expanded role under the GDPR” and a “significantly increased workload”.
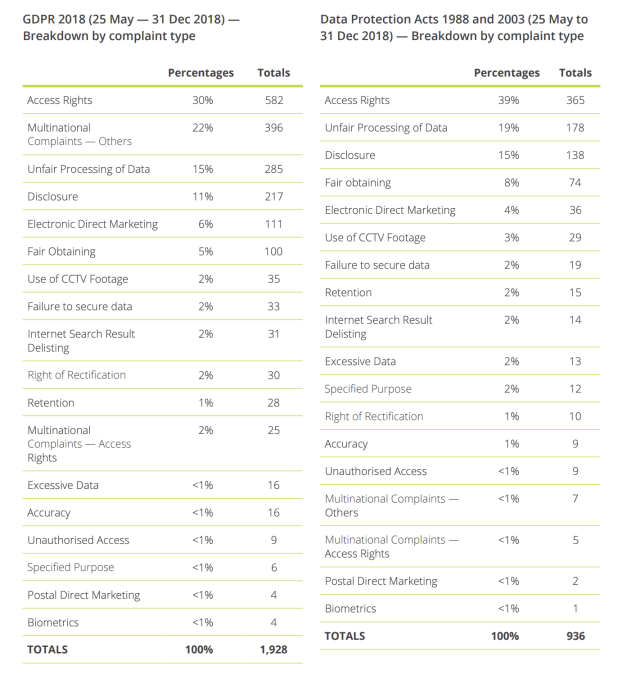
A breakdown of GDPR vs Data Protection Act 1998 complaint types over the report period suggests complaints targeted at multinational entities have leapt up under the new DP regime.
For some complaint types the old rules resulted in just 2 per cent of complaints being targeted at multinationals vs close to a quarter (22 per cent) in the same categories under GDPR.
It’s the most marked difference between the old rules and the new — underlining the DPC’s expanded workload in acting as a hub (and often lead supervisory agency) for cross-border complaints under GDPR’s one-stop shop mechanism.
The category with the largest proportions of complaints under GDPR over the report period was access rights (30%) — with the DPC receiving a full 582 complaints related to people feeling they’re not getting their due data. Access rights was also most complained about under the prior data rules over this period.
Other prominent complaint types continue to be unfair processing of data (285 GDPR complaints vs 178 under the DPA); disclosure (217 vs 138); and electronic direct marketing (111 vs 36).
EU policymakers’ intent with GDPR is to redress the imbalance of weakly enforced rights — including by creating new opportunities for enforcement via a regime of supersized fines. (GDPR allows for penalties as high as up to 4 per cent of annual turnover, and in January the French data watchdog slapped Google with a $57M GDPR penalty related to transparency and consent — albeit still far off that theoretical maximum.)
Importantly, the regulation also introduced a collective redress option which has been adopted by some EU Member States.
This allows for third party organizations such as consumer rights groups to lodge data protection complaints on individuals’ behalf. The provision has led to a number of strategic complaints being filed by organized experts since last May (including in the case of the aforementioned Google fine) — spinning up momentum for collective consumer action to counter rights erosion. Again that’s important in a complex area that remains difficult for consumers to navigate without expert help.
For upheld complaints the GDPR ‘nuclear option’ is not fines though; it’s the ability for data protection agencies to order data controllers to stop processing data.
That remains the most significant tool in the regulatory toolbox. And depending on the outcome of various ongoing strategic GDPR complaints it could prove hugely significant in reshaping what data experts believe are systematic privacy incursions by adtech platform giants.
And while well-resourced tech giants may be able to factor in even very meaty financial penalties, as just a cost of doing a very lucrative business, data-focused business models could be far more precarious if processors can suddenly be slapped with an order to limit or even cease processing data. (As indeed Facebook’s business just has in Germany, where antitrust regulators have been liaising with privacy watchdogs.)
Data breach notifications also up
GDPR also shines a major spotlight on security — requiring privacy by design and default and introducing a universal requirement for swiftly reporting data breaches across the bloc, again with very stiff penalties for non-compliance.
On the data breach front, the Irish DPC says it received a total of 3,687 data breach notifications between May 25 and December 31 last year — finding just four per cent (145 cases) did not meet the definition of a personal-data breach set out in GDPR. That means it recorded a total of 3,542 valid data protection breaches over the report period — which it says represents an increase of 27 per cent on 2017 breach report figures.
“As in other years, the highest category of data breaches notified under the GDPR were classified as Unauthorised Disclosures and accounted for just under 85% of the total data-breach notifications received between 25 May and 31 December 2018,” it notes, adding: “The majority occurred in the private sector (2,070).”
More than 4,000 data breach notifications were recorded by the watchdog for full year 2018, the report also states.
The DPC further reveals that it was notified of 38 personal data breaches involving 11 multinational technology companies during the post-GDPR period of 2018. Which means breaches involving tech giants.
“A substantial number of these notifications involved the unauthorised disclosure of, and unauthorised access to, personal data as a result of bugs in software supplied by data processors engaged by the organisations,” it writes, saying it opened several investigations as a result (such as following the Facebook Token breach in September 2018).
Open probes of tech giants
As of 31 December 2018, the DPC says it had 15 investigations open in relation to multinational tech companies’ compliance with GDPR.
Below is the full list of the DPC’s currently open investigations of multinationals — including the tech giant under scrutiny; the origin of the inquiry; and the issues being examined:
- Facebook Ireland Limited — Complaint-based inquiry: “Right of Access and Data Portability. Examining whether Facebook has discharged its GDPR obligations in respect of the right of access to personal data in the Facebook ‘Hive’ database and portability of “observed” personal data”
- Facebook Ireland Limited — Complaint-based inquiry: “Lawful basis for processing in relation to Facebook’s Terms of Service and Data Policy. Examining whether Facebook has discharged its GDPR obligations in respect of the lawful basis on which it relies to process personal data of individuals using the Facebook platform.”
- Facebook Ireland Limited — Complaint-based inquiry: “Lawful basis for processing. Examining whether Facebook has discharged its GDPR obligations in respect of the lawful basis on which it relies to process personal data in the context of behavioural analysis and targeted advertising on its platform.”
- Facebook Ireland Limited — Own-volition inquiry: “Facebook September 2018 token breach. Examining whether Facebook Ireland has discharged its GDPR obligations to implement organisational and technical measures to secure and safeguard the personal data of its users.”
- Facebook Ireland Limited — Own-volition inquiry: “Facebook September 2018 token breach. Examining Facebook’s compliance with the GDPR’s breach notification obligations.”
- Facebook Inc. — Own-volition inquiry: “Facebook September 2018 token breach. Examining whether Facebook Inc. has discharged its GDPR obligations to implement organizational and technical measures to secure and safeguard the personal data of its users.”
- Facebook Ireland Limited — Own-volition inquiry: “Commenced in response to large number of breaches notified to the DPC during the period since 25 May 2018 (separate to the token breach). Examining whether Facebook has discharged its GDPR obligations to implement organisational and technical measures to secure and safeguard the personal data of its users.”
- Instagram (Facebook Ireland Limited) — Complaint-based inquiry: “Lawful basis for processing in relation to Instagram’s Terms of Use and Data Policy. Examining whether Instagram has discharged its GDPR obligations in respect of the lawful basis on which it relies to process personal data of individuals using the Instagram platform.”
- WhatsApp Ireland Limited — Complaint-based inquiry: “Lawful basis for processing in relation to WhatsApp’s Terms of Service and Privacy Policy. Examining whether WhatsApp has discharged its GDPR obligations in respect of the lawful basis on which it relies to process personal data of individuals using the WhatsApp platform.”
- WhatsApp Ireland Limited — Own-volition inquiry: “Transparency. Examining whether WhatsApp has discharged its GDPR transparency obligations with regard to the provision of information and the transparency of that information to both users and non-users of WhatsApp’s services, including information provided to data subjects about the processing of information between WhatsApp and other Facebook companies.”
- Twitter International Company — Complaint-based inquiry: “Right of Access. Examining whether Twitter has discharged its obligations in respect of the right of access to links accessed on Twitter.”
- Twitter International Company — Own-volition inquiry: “Commenced in response to the large number of breaches notified to the DPC during the period since 25 May 2018. Examining whether Twitter has discharged its GDPR obligations to implement organisational and technical measures to secure and safeguard the personal data of its users.”
- LinkedIn Ireland Unlimited Company — Complaint-based inquiry: “Lawful basis for processing. Examining whether LinkedIn has discharged its GDPR obligations in respect of the lawful basis on which it relies to process personal data in the context of behavioural analysis and targeted advertising on its platform.”
- Apple Distribution International — Complaint-based inquiry: “Lawful basis for processing. Examining whether Apple has discharged its GDPR obligations in respect of the lawful basis on which it relies to process personal data in the context of behavioural analysis and targeted advertising on its platform.”
- Apple Distribution International — Complaint-based inquiry: “Transparency. Examining whether Apple has discharged its GDPR transparency obligations in respect of the information contained in its privacy policy and online documents regarding the processing of personal data of users of its services.”
“The DPC’s role in supervising the data-processing operations of the numerous large data-rich multinational companies — including technology internet and social media companies — with EU headquarters located in Ireland changed immeasurably on 25 May 2018,” the watchdog acknowledges.
“For many, including Apple, Facebook, Microsoft, Twitter, Dropbox, Airbnb, LinkedIn, Oath [disclosure: TechCrunch is owned by Verizon Media Group; aka Oath/AOL], WhatsApp, MTCH Technology and Yelp, the DPC acts as lead supervisory authority under the GDPR OSS [one-stop shop] facility.”
The DPC notes in the report that between May 25 and December 31 2018 it received 136 cross-border processing complaints through the regulation’s OSS mechanism (i.e. which had been lodged by individuals with other EU data protection authorities).
A breakdown of these (likely) tech giant focused GDPR complaints shows a strong focus on consent, right of erasure, right of access and the lawfulness of data processing:
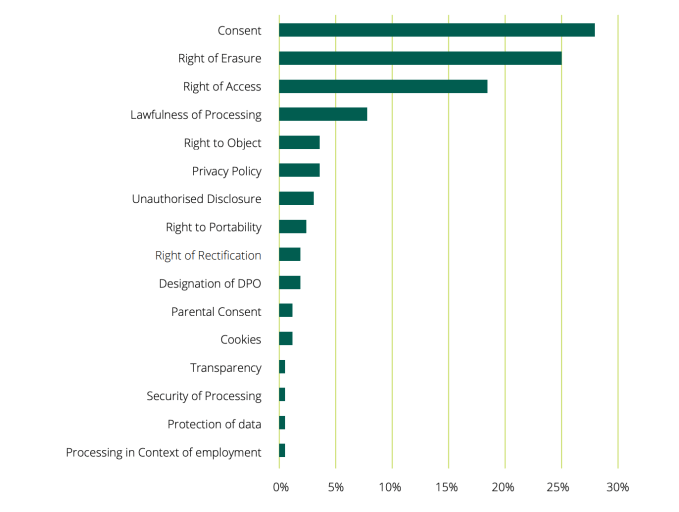
Breakdown of cross-border complaint types received by the DPC under GDPR’s OSS mechanism
While the Irish DPC acts as the lead supervisor for many high profile GDPR complaints which relate to how tech giants are handling people’s data, it’s worth emphasizing that the OSS mechanism does not mean Ireland is sitting in sole judgement on Silicon Valley’s giants’ rights incursions in Europe.
The mechanism allows for other DPAs to be involved in these cross-border complaints.
And the European Data Protection Board, the body that works with all the EU Member States’ DPAs to help ensure consistent application of the regulation, can trigger a dispute resolution process if a lead agency considers it cannot implement a concerned agency objection. The aim is to work against forum shopping.
In a section on “EU cooperation”, the DPC further writes:
Our fellow EU regulators, alongside whom we sit on the European Data Protection Board (EDPB), follow the activities and results of the Irish DPC closely, given that a significant number of people in every EU member state are potentially impacted by processing activities of the internet companies located in Ireland. EDPB activity is intense, with monthly plenary meetings and a new system of online data sharing in relation to cross-border processing cases rolled out between the authorities. The DPC has led on the development of EDPB guidance on arrangements for Codes of Conduct under the GDPR and these should be approved and published by the EDPB in Q1 of 2019. The DPC looks forward to industry embracing Codes of Conduct and raising the bar in individual sectors in terms of standards of data protection and transparency. Codes of Conduct are important because they will more comprehensively reflect the context and reality of data-processing activities in a given sector and provide clarity to those who sign up to the standards that need to be attained in addition to external monitoring by an independent body. It is clarity of standards that will drive real results.
Over the reported period the watchdog also reveals that it issued 23 formal requests seeking detailed information on compliance with various aspects of the GDPR from tech giants, noting too that since May 25 it has engaged with platforms on “a broad range of issues” — citing the following examples to give a flavor of these concerns:
- Google on the processing of location data
- Facebook on issues such as the transfer of personal data from third-party apps to Facebook and Facebook’s collaboration with external researchers
- Microsoft on the processing of telemetry data collected by its Office product
- WhatsApp on matters relating to the sharing of personal data with other Facebook companies
“Supervision engagement with these companies on
source https://techcrunch.com/2019/02/28/privacy-complaints-received-by-tech-giants-favorite-eu-watchdog-up-more-than-2x-since-gdpr/
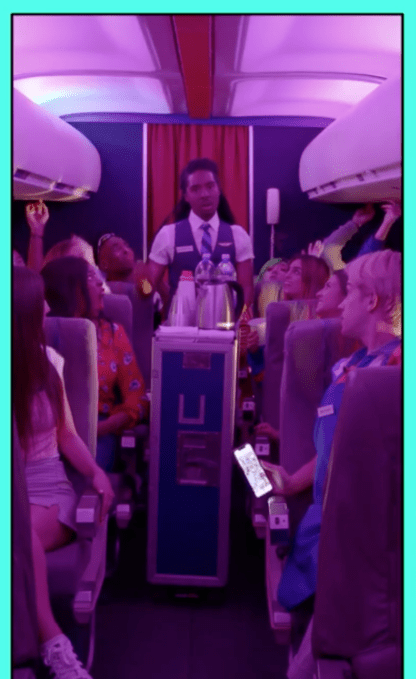





 “Too many DMs?,” the video asks. The flight attendant snaps his fingers, which causes most of the passengers to disappear. The scene returns to peace and quiet. It’s a simple enough analogy for TikTok’s younger user base to understand.
“Too many DMs?,” the video asks. The flight attendant snaps his fingers, which causes most of the passengers to disappear. The scene returns to peace and quiet. It’s a simple enough analogy for TikTok’s younger user base to understand. At launch, there are seven of these short-form videos in the safety series, which will launch in the TikTok app in the U.S. and U.K on Wednesday. In time, the company plans to add other tutorials and expand the series across its global markets, it says.
At launch, there are seven of these short-form videos in the safety series, which will launch in the TikTok app in the U.S. and U.K on Wednesday. In time, the company plans to add other tutorials and expand the series across its global markets, it says.